Galvanic isolation refers to the principle in which two circuits are electrically completely isolated from each other, although signals or energy can still be transmitted between them. This is usually done by components such as transformers, optocouplers or special coupling elements that do not use a direct electrical connection, but rather a magnetic or optical coupling, for example.
Galvanic isolation on the USB port makes sense for several reasons and has both safety and practical advantages.
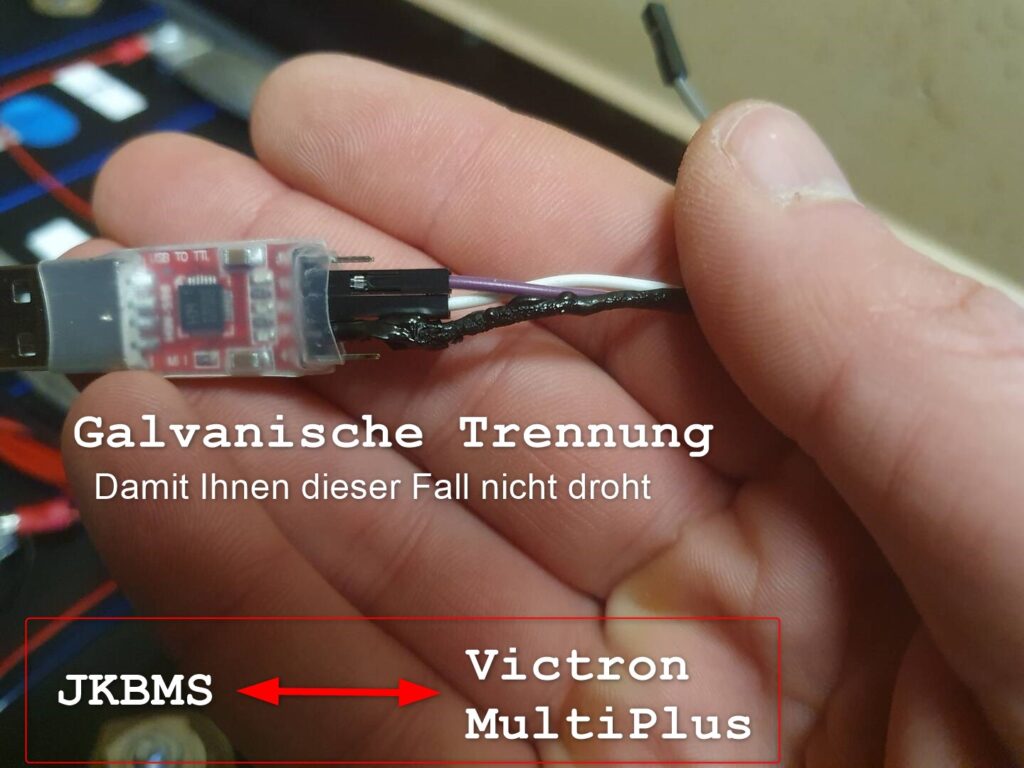
Protection against voltage differences and overvoltage.
USB connections normally provide a direct electrical connection between the PC (host) and connected devices. If overvoltages occur due to lightning strikes, switching operations or electrostatic discharge, dangerous equalizing currents can flow, which can cause irreparable damage to the hardware. Galvanic isolation prevents such voltage peaks or potential differences from being passed from one device to another.
The picture shows scorched cable parts. Here, excessive currents from a correctly connected JKBMS to a 16s battery (48V) caused the damage. The FT232 adapter was destroyed. Fortunately, not the USB port or the board of the Victron Multiplus 2.
Use our galvanically isolated adapter with FT232RL chip. Order here.
